We’ve talked about cloud computing several times here at Computer Answers. The applications and benefits of this network in the clouds have been discussed and debated.
Wikibon has created several infographics looking at private versus public cloud computing. Among other things, the infographic shows that public cloud computing costs $638 per seat organizations more than private computing. Most of that cost comes from outsourcing. Before getting into the charts, let's start with some basics.
Cloud Computing & Its Characteristics
Before understanding the characteristics of cloud computing, we need to understand what cloud computing is. Cloud computing refers to the on-demand accessibility of computer system services, particularly data storage and computational power, without the need for the user to actively manage them. Functions in large clouds are frequently dispersed across numerous locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on resource sharing to accomplish coherence and economies of scale, often through a "pay-as-you-go" approach, reducing capital expenses and exposing users to unanticipated running expenses.
Self-service on-demand. Cloud computing services can be supplied without human contact from the service provider. To put it another way, a manufacturing company can increase computing resources as needed without going via a cloud service provider. It could be a storage space, virtual machine, database, or something else entirely.
Cloud computing may promote organizational agility by allowing users more freedom in re-provisioning, adding, or expanding technological infrastructure resources.
Fast scalability and flexibility. One of the most appealing aspects of cloud computing is the ability to supply cloud services as needed for industrial companies swiftly. When they are no longer needed, they should be removed. Cloud computing resources can be instantly and, in some situations, automatically scaled up or down in response to business needs. It's a crucial aspect of cloud computing.
The management of a cloud system is simplified because the data is stored on an external server operated by a provider, eliminating the necessity to invest in data center hardware. In addition, when opposed to on-premises data centers, cloud computing IT maintenance is handled and upgraded by the cloud provider's IT, maintenance team, lowering cloud computing costs.
Cloud computing resources support a multi-tenant approach. Multi-tenancy permits multiple clients to access the same apps or physical infrastructure while maintaining their privacy and security. It's like folks who live in an apartment building who share the same infrastructure but have their apartments and privacy within that infrastructure. This is how multi-tenancy in the cloud works.
Productivity may be boosted when various users operate on the same data simultaneously, rather than relying on it to be recorded and emailed. Users don't have to re-enter information when fields are matched, and they don't have to install application software upgrades on their computers, which saves time.
Device and location independence allow people to reach systems using a web browser independent of their location or device. Users can connect to infrastructure from anywhere because it is off-site, often provided by a third party, and accessible via the Internet.
Risks of Cloud Computing
Though the characteristics of cloud computing are appealing, there are some risks of cloud computing associated with it. Cloud computing offers several benefits, like increased collaboration, excellent accessibility, mobility, and storage capacity, to name a few. Cloud computing, however, comes with its own set of security concerns.
The following are some of the most common security risks associated with cloud computing:
Data loss
Data loss is one of the most prominent cloud security concerns. It's sometimes referred to as data leakage. Data loss occurs when data is accidentally destroyed, corrupted, or rendered unreadable by a person, software, or application. Data loss occurs in a cloud computing environment when our sensitive data is in the hands of others, one or more data elements are unavailable to the data owner, the hard disk is not functioning properly, and software is not updated.
Hacked Interfaces and Insecure APIs
Because cloud computing is entirely reliant on the Internet, external users' interfaces and APIs must be protected. APIs are the most convenient way to interact with most cloud services. Unfortunately, only a few cloud computing services are open to the public. Because third parties can access these services, there is a risk of being harmed or compromised by hackers.
Data Breach
Data Breach is the process through which confidential data is viewed, accessed, or taken by a third party without authorization, resulting in the hacking of an organization's data.
Account Hijacking
In cloud computing, account hijacking is a severe security concern. It is the act of hackers stealing a user's or an institution's cloud account (bank account, email account, or social media account). Then, hackers exploit the hacked account to carry out illegal acts.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
A denial of service (DoS) attack occurs when a network gets too much traffic to buffer a denial of service (DoS) attack. DoS attacks are most commonly directed at web servers of large businesses, such as banks, media firms, and government agencies. DoS attackers charge a significant amount of time and money to retrieve the lost data.

Via: Public Versus Private Cloud Computing
Another infographic shows that 1,000 traditional servers (small stand- alone data centers) cost a business $3,350,000 while 1,000 cloud based servers (1,000 within 1000,000 servers) only cost $798,000.
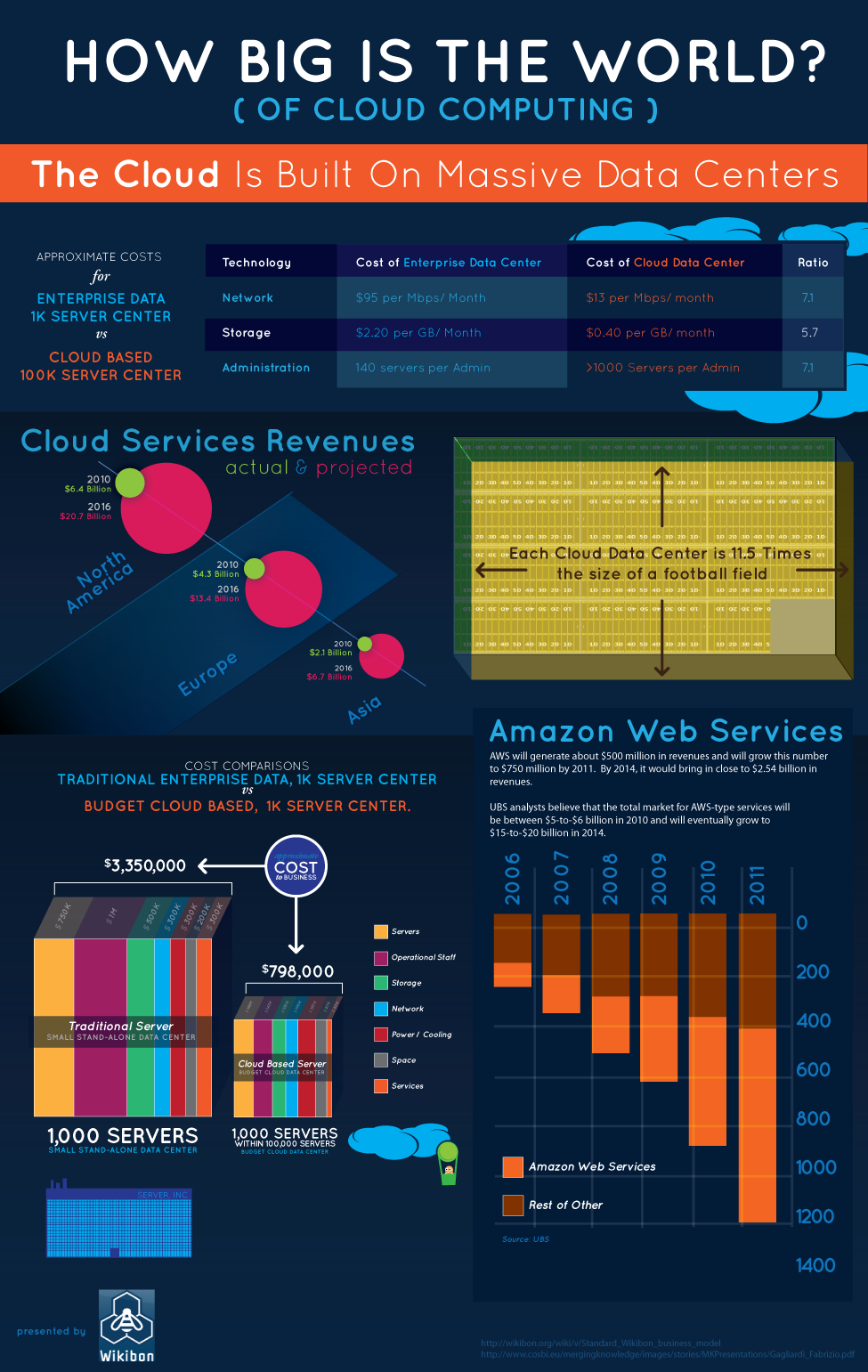 Via: Wikibon
Via: Wikibon
If your company does a lot of online business, Cloud computing could save you hundreds of thousands of dollars over the years
Why You’ll Love Moving Your Files to The Cloud
That’s reason enough to make the switch to a cloud system, of course, but we’ve noticed something interesting recently as great as the bottom-line savings of cloud computing are, there are other benefits that clients come to love even more:
Automatic software updates. Instead of having to manually approve software updates or worse, carry disks from one computer to the next cloud computing lets software packages update automatically on host servers. That means less work and better performance for every application you use.
Real-time file sharing and collaboration. If you have remote employees, multiple office locations, or vendors you work with frequently, then the instantaneous nature of cloud communications can save you a lot of time and stress. Forget about endless e-mails and phone calls back and forth, because multiple people can work on the same files simultaneously.
Better data security. Executives sometimes worry that cloud computing is less safe than keeping files on-site, but the opposite is true: With encrypted transfers, continuous power backup, trained cloud engineers monitoring the facility, and on-site security, your information (and your customers’ data) has never been safer.
Could these advantages help make your business more profitable?
Share This.



 Via:
Via: